Trimming is a common process in the production of rubber products. Trimming methods include manual trimming, grinding, cutting, cryogenic trimming, and flashless mold forming, among others. Manufacturers can choose the appropriate trimming method based on the quality requirements of the products and their own production conditions.

Manual Trimming
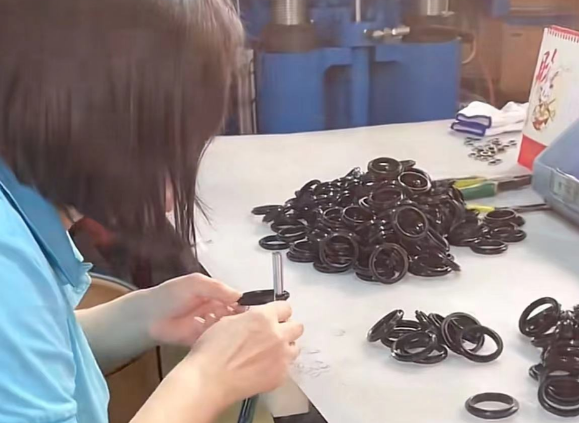
Manual trimming is an ancient method of trimming, which involves manually punching and cutting the rubber edge using punches, scissors, and scraping tools. The quality and speed of manually trimmed rubber products can vary from person to person. It is required that the geometric dimensions of the products after trimming must meet the requirements of the product drawings, and there should be no scratches, cuts, or deformations. Before trimming, it is necessary to clearly understand the trimming area and technical requirements, and to master the correct trimming methods and the proper use of tools.
In the production of rubber parts, most of the trimming operations are carried out through various forms of manual operations. Due to the low production efficiency of manual trimming operations, it is often necessary to mobilize many people for trimming, especially when production tasks are concentrated. This not only affects the work order but also compromises the quality of the products.

Mechanical Trimming
Mechanical trimming mainly includes punching, grinding with a grinding wheel, and circular blade trimming, which are suitable for specific products with low precision requirements. It is currently an advanced trimming method.
1) Mechanical punching trimming involves using a press machine and a punch or die to remove the rubber edge of the product. This method is suitable for products and their rubber edges that can be placed on the punch or die base plate, such as bottle stoppers, rubber bowls, etc. For products with a high rubber content and low hardness, the impact method is usually used to trim the edges, which can reduce the unevenness and depression on the side surface caused by the elasticity of the product after cutting. For products with low rubber content and high hardness, the method of using a cutting edge mold can be directly adopted. In addition, punching can be divided into cold punching and hot punching. Cold punching refers to punching at room temperature, requiring higher punching pressure and better punching quality. Hot punching refers to punching at a higher temperature, and it is necessary to avoid prolonged contact with the product at high temperatures, which may affect the quality of the product.
2) Mechanical cutting trimming is suitable for trimming large-sized products and uses cutting tools. Each cutting machine is a special machine, and different products use different cutting tools. For example, after the tire is vulcanized, there are rubber strips of different lengths on the surface vents and exhaust lines of the tire, which need to be removed using a grooved tool while the tire is rotating.
3) Mechanical grinding trimming is used for rubber products with internal holes and outer circles, and grinding is usually used. The grinding tool is a grinding wheel with certain particle size, and the precision of grinding trimming is low, resulting in a rough surface and possible residual sand particles, which may affect the application effect.
4) Cryogenic deflashing is used for precision products with high trimming quality requirements, such as O-rings, small rubber bowls, etc. This method involves rapidly cooling the product to a brittle temperature using liquid nitrogen or dry ice, and then rapidly injecting metal or plastic pellets to break and remove the flash, completing the trimming process.
5) Low-temperature brushing trimming: It involves using two nylon brushes rotating around a horizontal axis to brush off the rubber edge of frozen rubber products.
6) Low-temperature drum trimming: This is the earliest method of cryogenic trimming, using the impact force generated by the rotating drum and the friction between the products to crack and remove the flash from the products that have been frozen below the embrittlement temperature. The shape of the drum is usually octagonal to increase the impact force on the products in the drum. The drum speed should be moderate, and the addition of abrasives can improve efficiency. For example, the edge trimming technique of rubber plugs for electrolytic capacitors uses low-temperature drum trimming.
7) Low-temperature oscillating trimming, also known as oscillating cryogenic trimming: The products oscillate in a spiral pattern in a circular sealing box, resulting in strong impact between the products and between the products and the abrasive, causing the frozen flash to fall off. Low-temperature oscillating trimming is better than low-temperature drum trimming, with lower product damage rates and higher production efficiency.
8) Low-temperature rocking and vibrating trimming: It is suitable for small or miniature products or micro silicone rubber products rich in metal skeletons. It is used together with abrasives to remove the flash from the product holes, corners, and grooves.
Cryogenic Deflashing Machine
The specialized cryogenic deflashing machine removes burrs by using liquid nitrogen to make the edges of the finished product brittle at low temperatures. It uses specific frozen particles (pellets) to quickly remove the burrs. The frozen edge trimming machine has high production efficiency, low labor intensity, good trimming quality, and a high degree of automation, making it particularly suitable for pure rubber parts. It is widely applicable and has become the mainstream process standard, suitable for removing burrs from various rubber, silicone, and zinc-magnesium-aluminum alloy parts.
Burrless mold
Using burrless molds for production makes the trimming work simple and easy (the burrs can be easily removed by tearing, so this type of mold is also called a tear-off mold). The burrless mold forming method completely eliminates the trimming process, improves product quality and performance, reduces labor intensity, and production costs. It has broad development prospects but is not suitable for manufacturers with flexible and diverse products.
Post time: Sep-05-2024